Heat pumps are widely known for their heating and cooling applications in the residential sector, but they are still under-deployed in industrial applications. In fact, many industries can economically benefit from the installation of this technology. Heat pumps provide heating and cooling, using waste energy from processes. Increasing the energy efficiency of an industrial process, by installing a heat pump, will result both in cost reductions for the industry and in positive environmental impacts for the whole society.
Today, heat pumps are already used in a wide variety of applications especially in sectors like food & beverage, wood & paper or chemical and district heating, pushing further and further the research of more performant solutions. Find 16 examples of realized and successful projects here.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
Industrial heat pumps actively recover waste heat. The system is rather simple: heat pumps increase the temperature of waste heat streams to a higher temperature, making those steams usable again.
The heat pump operates on the basis of a working fluid (refrigerant) which changes state (liquid/gas) in a continuous cycle and absorbs and releases heat (Carnot cycle).
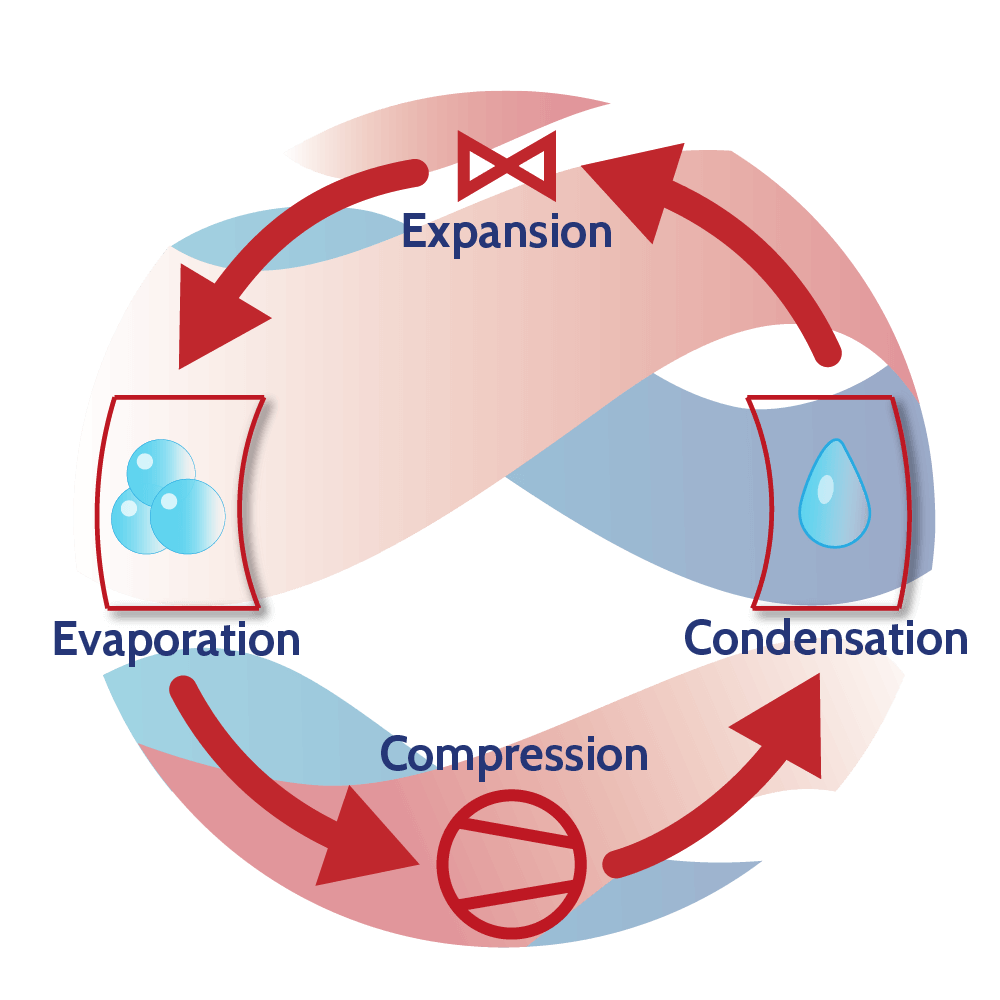
- Evaporation: In the evaporator, the refrigerant is exposed to the heat source (e.g. industrial waste heat). There, the refrigerant evaporates at low pressure and low temperature.
- Compression: The compressor increases the pressure of the refrigerant to a higher pressure level.
- Condensation: In the condenser, the energy of the working fluid (refrigerant) is transferred to a distribution medium (e.g. air) or a heat consumer. The refrigerant is cooled and becomes liquid again.
- Expansion: In order to close the heat pump loop, the working fluid is fed into an expansion valve. The low pressure low temperature liquid is ready to enter the evaporator again.
Heat pumps can find application in numerous industrial processes and are particularly efficient when direct heat exchange is not possible, going even beyond a closed circuit and allowing the creation of integrated system with different processes or users.
WASTE HEAT SOURCES THAT CAN BE VALORIZED WITH HEAT PUMPS
- Waste water
- Humid off gases from drying processes
- Water streams that need to be cooled before further treatment
- Waste heat from chillers (refrigeration)
- Processes that require cooling
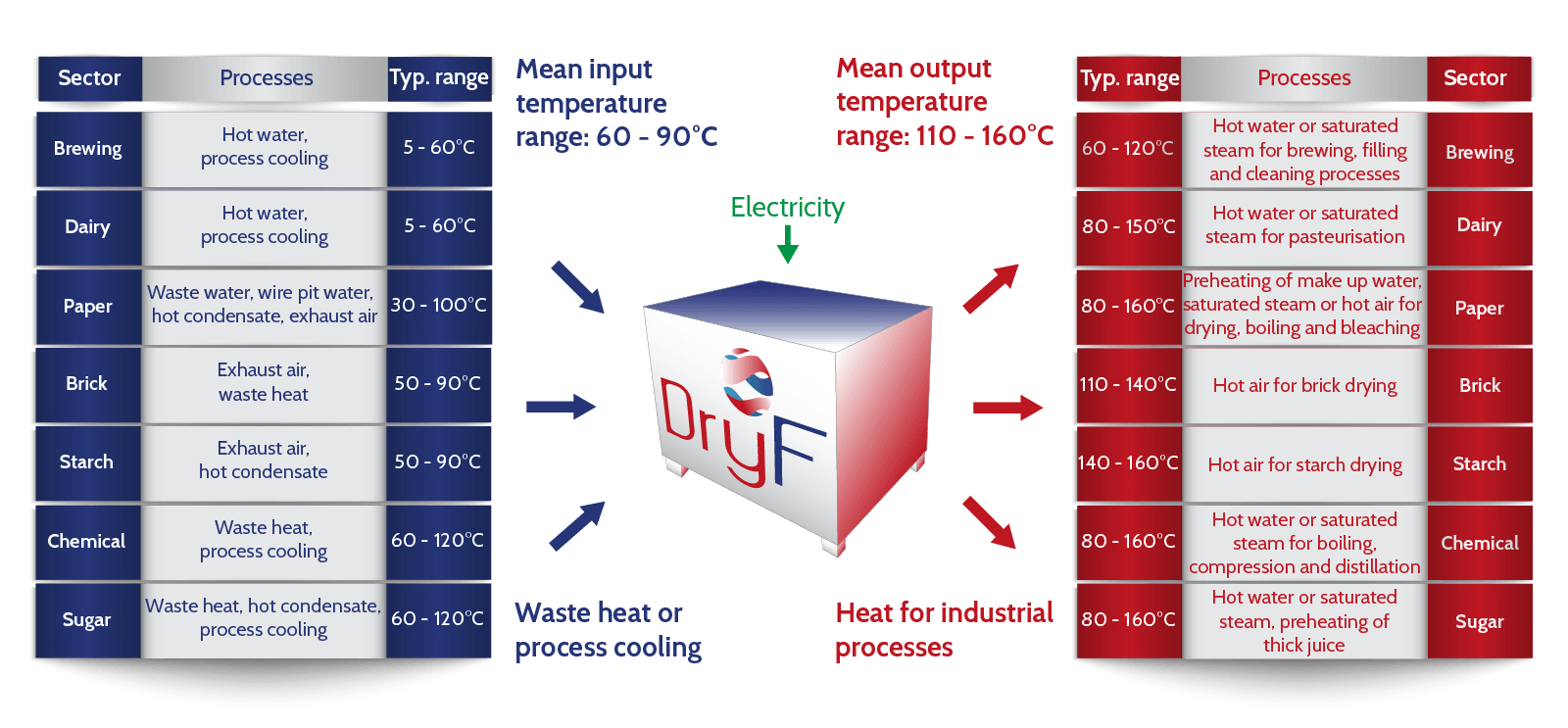
TYPICAL PROCESSES
Industrial plants provide a wide variety of heat sources and potential users; thus, there are various applications for industrial heat pumps. Those are some examples:
- Drying and dehydration
- Evaporation
- Washing, cleaning
- Cooking
- Sterilization, pasteurisation
- Space heating
- District heating
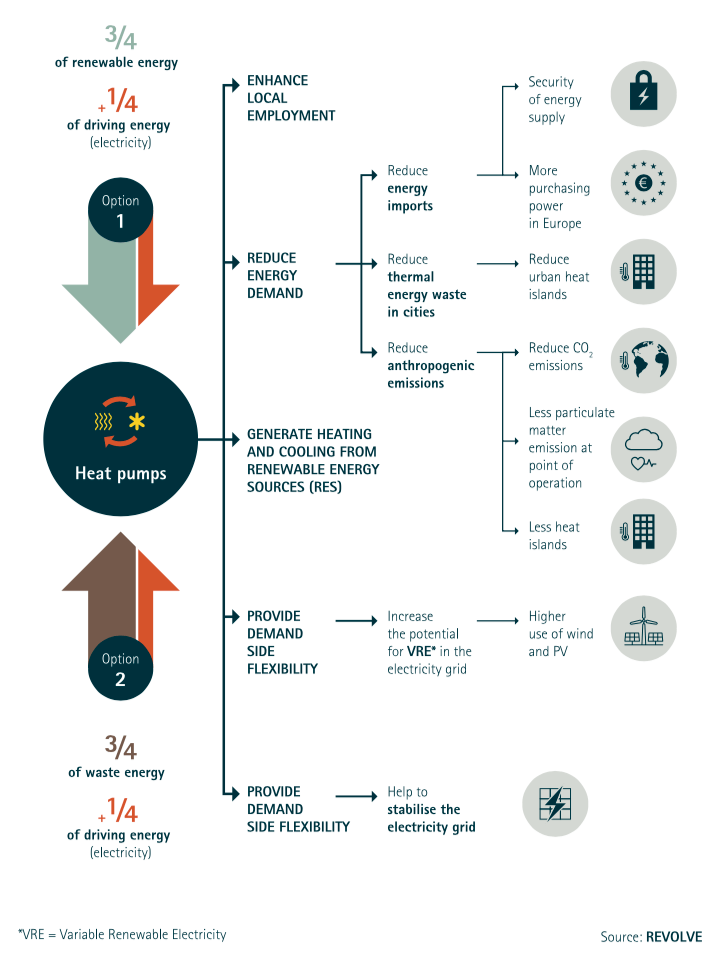
THE ADDED VALUE OF HEAT PUMP TECHNOLOGY
Heat pump technology delivers major economic, environmental and societal benefits to society.
More information is provided in the White Paper: Heat pumps – Integrating Technologies to Decarbonise Heating and Cooling here.



